How to Write a Content Brief [Template + Examples]
I’ve worked in a lot of different industries — as a freelancer, as a manager of freelancers, as a marketer, as a writer — and you know what never changes? The need for content creators to be crystal clear on their assignments.
One of the simplest ways to achieve this is to write content briefs.
Don’t be deceived, though: Even though a content brief is simple, it’s still important to get it right.
Table of Contents
What is a content brief?
A content brief is a short document — if you can keep it to a page or two, everybody will be happy — that’s a guide or blueprint for creating content.
The specifics will vary depending on the kind of content you’re creating and who the brief is for, but it should anticipate and answer top-level questions about content, format, communication, and so forth.
If you manage freelance writers, a content brief will be a lifesaver for both you and your writers — and that’s only a slight exaggeration. Your content briefs will describe exactly what’s expected of the writer, including any required subheadings, target word count, and deadlines.
If you work on a project with multiple partners at multiple organizations, a simple content brief will give everybody a single source of truth.
Content Briefs vs. Creative Briefs
Although they sound similar, content briefs and creative briefs serve different purposes. A creative brief outlines a campaign, and may include more extensive messaging, deliverables from multiple contributors, and other details that give shape to the entire campaign.
A content brief focuses on a specific piece of content — my examples below are for written content, but you could use the same elements to create a content brief for videos, podcasts, or anything else you’re producing. If you’re using software like Content Hub, a brief will be the foundation for each piece of content.
Importance of Content Briefs
Sure, you could try to muddle through without one, but they save more time than they take to write.
I once worked on a project with several external partners, and other than Slack and Google Docs, nobody used the same organizational tools, and it caused a lot of frustration and confusion.
I pulled together a generic content brief that could be iterated on for specific assignments. It included approved messaging, links to all the documents that everybody was working on, and major deliverables and deadlines. You could almost hear the sigh of relief in the Slack channel.
I used to do some freelance writing, and my favorite client was the one that had the best content brief. Writing for a new client can be intimidating, even for experienced writers, because you have to learn a new style guide, a new voice, and maybe even an entirely new target audience.
That particular client included a one-page brief with each assignment. It included the target word count and the rate, the name of the publication and its audience, as well as links to the style guide and any assets, a description of the assignment, and the assigning editor and due date. If an interview was required, contact info was provided.
They were a dream to freelance for because I never wasted time with logistical questions — the expectations were clear and everything I needed was at my fingertips.
If you’re editing content, providing a clear content brief will reduce the number of revisions and rewrites (not to mention frustration!). Let’s talk about how to strike a balance between detailed and concise.
Elements of a Content Brief
The elements of a content brief will vary depending on your needs, but here are what I think are the absolute essentials:
- Point person and/or a responsibility matrix
- Communication protocols, such as a Slack channel
- Clear description of the project or assignment, including target audience and word count
- Links to assets, messaging, style and/or brand guides, and any other relevant shared documents
- Deliverables and deadlines

You might also include:
- Approved messaging and/or language from partners
- KPIs
- Funnel stage
- Links to similar content that can be used as a model or inspiration
- Links to the competition
- Links to audience personas
When I’ve worked on marketing multi-partner podcasts, I’ve found it helpful to include a few bullet points of approved messaging, noting who has approved on behalf of each partner.
Some stakeholders may have certain requirements for how their company or organization is described, and your writers and content marketers will need that info.
Keep it simple:

Pro tip: Especially when working with external partners, it’s often worth repeating important brand details that are in your style guide. Don’t get too bogged down here — the style guide exists for a reason — but stakeholders will appreciate having this info at hand.
If you’re writing content briefs for freelancers, you’ll want to make sure they have access to any information they might need during the course of their assignment — style or brand guidelines, Slack channels, who to contact with questions, and any context for the assignment.
Let’s dig into “clear description of the assignment,” since that can contain a lot of important details for your writer(s), such as:
- Purpose. Tell the writer what the content goal is; maybe it’s a blog post to address demand for a certain keyword, or maybe you need ad copy and a variety of CTAs for a new product.
- SEO/keywords. What does your writer need to know about target keywords? Are there any keywords or topics that they should avoid to prevent content cannibalization?
- Subject matter experts and sourcing. In our brave new E-E-A-Tified world, firsthand experience is more important than ever. If your writer is expected to conduct SME interviews, include that in the brief. You may also ask that they provide links to any other sources they’ve used to assist with any light fact-checking.
- Required subheadings and other technical specifications. If you’ve done your keyword research, you may already have H2 or H3 subheadings in mind. This will also help the writer understand how you want the content organized. Your writer may also be expected to provide meta descriptions, alt text for images, or social media copy.
- Other formatting requirements. If a document needs to be formatted in a certain way, explain how (ideally with an example or template). If you can only accept (or if you prefer) a certain file type, include that — don’t assume that everybody is using Google Workspace or Microsoft Word just because you are.
- Sharing/access requirements. We all know the frustration of seeing “Access denied.” Set everybody up for success by including info on who to share files with.
- How and where to file the completed assignment. Does your workflow require tagging certain people in an Asana card? Do writers email you when they’ve completed an assignment?
- Naming conventions. If any of the deliverables, including assets, need to follow a specific filename convention, lay that out in your content brief.
- Post-assignment expectations. If writers should expect to hear from an editor, let them know that ahead of time — freelancers in particular will need to budget time for this. And if you manage a large roster of freelancers, it can be helpful to include any reminders about the rate and invoicing requirements.
How to Write a Content Brief
Let’s make a template: Using your word processor of choice, create a one-page doc with a two-column table. In the left-hand column, write out the basic elements: point person and/or responsibility matrix, communication protocols, assignment description, assets, and deadlines and deliverables.
This is personal preference, but I like to list the communication info in the top left header of the brief, including the relevant Slack channel — I repeat this info when I have to create other docs for stakeholders, so everybody gets used to having it front and center.
It immediately answers the top questions: Who’s in charge? Who needs to provide approval? Where did you tell me that Google Drive was? Why didn’t anybody tell me there was a Slack channel for this project?
Even if this info feels redundant, it can be especially helpful for new freelancers or new hires, so I suggest making it part of your template. Freelancers often have several (or more) clients, all of whom might have different requirements and formats, and this will save them some time and sanity.
Your brief might start off like this:
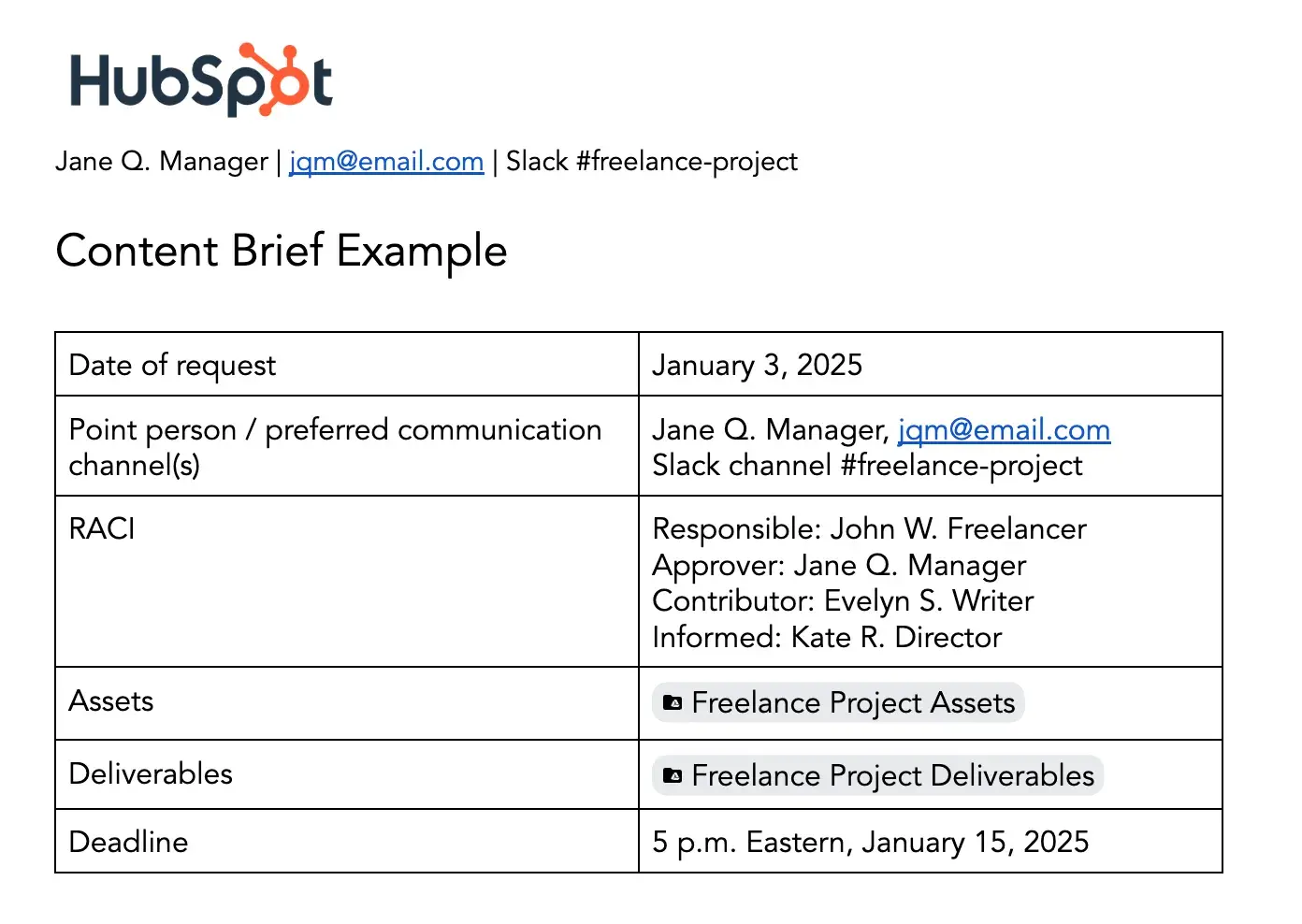
Pro tip: You’ll note that I’ve included the time and time zone in the due date — I consider this essential information. Especially in the age of distributed workforces, where employees and freelancers may be in different time zones, including this will save everybody a headache and set your writer up for success.
Before you flesh out any details in the assignment description, consider who your content brief is for. Freelance writers will likely need more links and more context than in-house writers, who already have the company style guide bookmarked (right? Right?).
You may find it useful to create two templates, one for in-house writers and one for freelancers, so you can provide your marketers with the most concise brief. For instance, freelancers may not need info on KPIs; in-house writers who upload their own work to the CMS won’t need a folder for deliverables.
What’s the absolute minimum information a writer needs to successfully complete an assignment? It’s tempting to include links to everything related to the project, but don’t overload your writers with unnecessary context.
It’ll be useful at this stage to talk to them, whether they’re in-house or freelance, and find out what they find most helpful.
You’ll need to describe the assignment, its purpose, and its audience:

Pro tip: For freelancers, consider always including a link to your style guide. That way it’s always handy. And a simple “thank you” is always a nice touch.
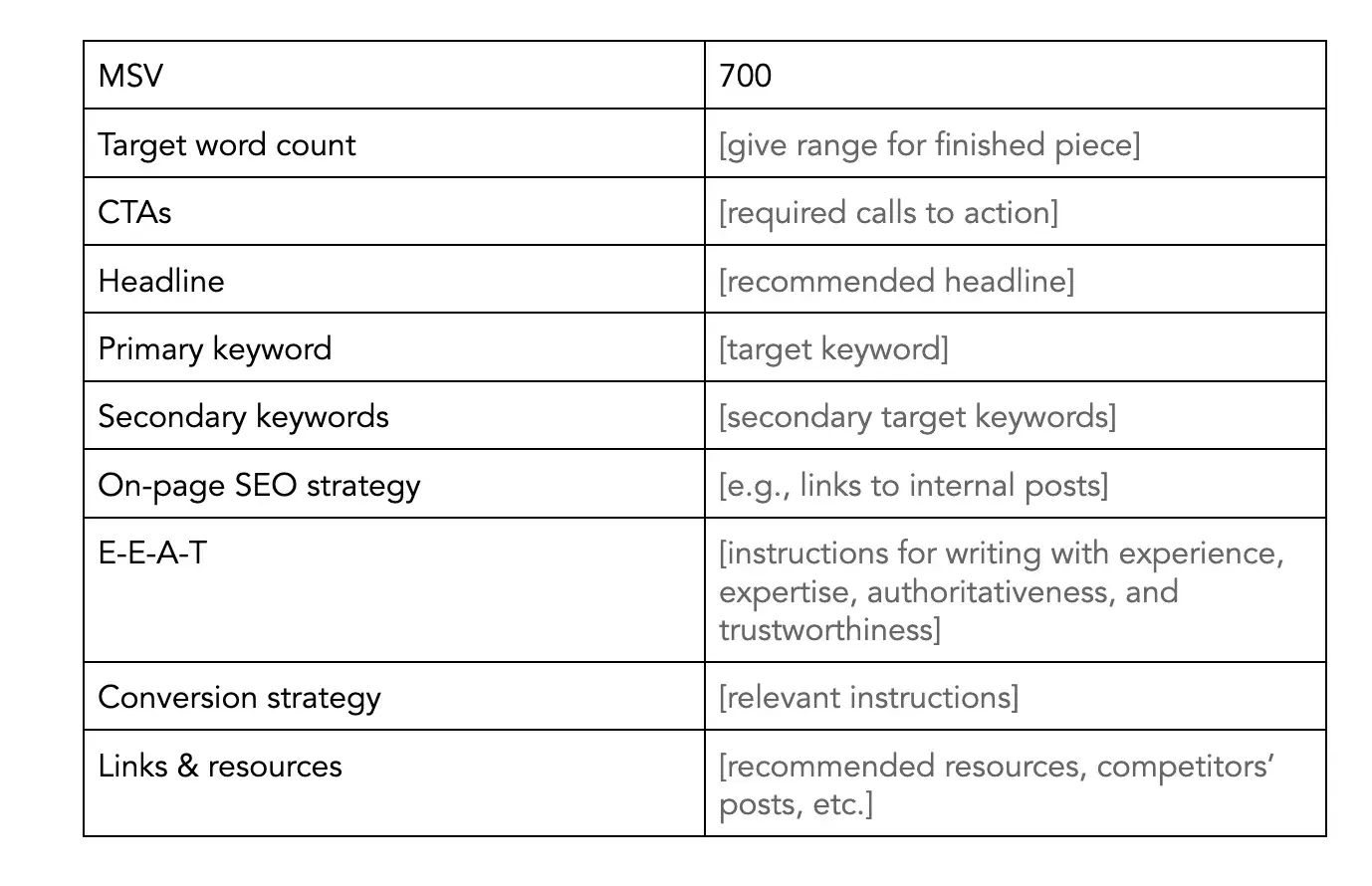
If your content has a lot of specific requirements for conversion strategy, SEO, keywords, and the like, include those in a table so they’re easy to parse.
When I worked as a freelance writer, I found this incredibly helpful. It’s a small thing, but being able to see all this info in the same format with each assignment makes it much easier to get started on assignments.
Info that’s often included in HubSpot assignments is the monthly search volume, any required CTAs, and SEO and conversion strategies:
Write Your First Content Brief
Once you’ve built a template (or two) that suits your needs, content briefs won’t take you much time at all to fill out. And whether you’re working with in-house content creators, freelancers, and/or external stakeholders, having a single source of information will make everybody’s job easier and more efficient.
![]()

